کیلٹی بولیاں
| کیلٹک | |
|---|---|
| جغرافیائی تقسیم: | یورپ وچ سابقہ طور اُتے وچ وڈے پیمانے پر; ہن کورنوال، ویلز، اسکاٹ لینڈ، جزیرہ آئرلینڈ، بریتانیہ، پیٹاگونیا، نووا سکوشیا تے آئل آف مین |
| لسانی درجہ بندی: | ہند۔یورپی
|
| سابقہ اصل-زبان: | پروٹو-کیلٹک |
| ذیلی تقسیمات: |
|
| آیزو 639-2 / 5: | cel |
| کرہ لسانی: | 50= (phylozone) |
| گلوٹولاگ: | celt1248[۱] |
 Distribution of Celtic speakers:
Hallstatt culture area, 6th century BC
Maximal Celtic expansion, c. 275 BC
Lusitanian area; Celtic affiliation doubtful
Areas where Celtic languages are widely spoken in the 21st century | |
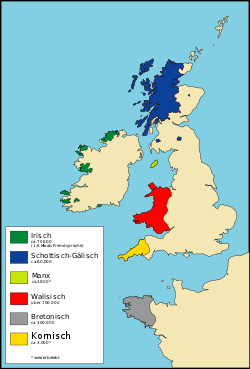
کیلٹی بولیاں ہند یورپی بولیاں اندر بولیاں دا اک ٹبر اے۔ ایدے چ ویلزی، بریطانی، آئرش، مانکس بولی، تے سکاٹ گالی بولیاں آندیاں نیں۔ ایہ آئرلینڈ برطانیہ تے فرانس چ بولیاں جاندیاں نیں۔
کیلٹک زباناں (Celtic languages) (عمومی تلفظ: /ˈkɛltɪk/ کیلٹک لیکن کدی کدائيں /ˈsɛltɪk/) سیلٹک وی کہیا کاندا اے [۲] ہند۔یورپی لسانی خاندان [۳] دی شاخ پروٹو-کیلٹک زبان دی نسل توں اک بولی اے۔
جدید کیلٹک زباناں زیادہ تر یورپ دے شمال مغربی کنارے اُتے بولی جاندیاں نيں جس وچ جزیرہ آئرلینڈ، اسکاٹ لینڈ، ویلز، بریتانیہ، کورنوال تے آئل آف مین قابل ذکر نيں۔ ویلش بولنے والےآں دی اک وڈی تعداد ارجنٹائن دے علاقے پیٹاگونیا وچ وی موجود اے۔ اس دے علاوہ اسکاٹش گیلک بولنے والے کچھ لوک نووا سکوشیا وچ موجود نيں۔ کیلٹک زباناں بولنے والے کچھ تارکین وطن ریاستہائے متحدہ [۴]، کینیڈا، آسٹریلیا [۵] تے نیوزی لینڈ وچ وی موجود نيں۔
پہلے ہزارے ق م وچ ایہ یورپ، جزیرہ نما آئبیریا، بحراوقیانوس توں بحیرہ شمال دے ساحل تک، وادی رائن تے اور تھلے داودی ڈینیوب توں ہُندے ہوئے بحیرہ اسود تک، شمالی بلقان توں وسطی اناطولیہ تک بولی جادیاں سن۔
حیات زباناں
[سودھو]کئی کیلٹک زباناں معدوم ہوئے چکيتیاں نيں، چھ کیلٹک زباناں ایسی نيں جنہاں دے بولنے والے ہن وی وڈی تعداد وچ موجود نيں مندرجہ ذیل نيں۔
ان وچ گویڈیلک زباناں (آئرش، اسکاٹش گیلک) جو وسطی آئرش توں نکلی نيں تے بریطانی زباناں (ویلش تے بریٹن) جو عام بریطانی توں نکلی نيں۔
ہور دو کورنش (اک بریطانی زبان) تے مینکس (اک گویڈیلک زبان) جدید دور وچ معدوم ہوئے چکی ہی۔ [۶][۷][۸]
آبادیات
[سودھو]| زبان | مقامی نام | گروہ بندی | اصل بولنے والےآں دی تعداد | لوکاں دی تعداد جو بولی وچ اک یا زیادہ مہارت رکھدے نيں | بنیادی علاقے جتھے بولی بولی جاندی اے | لسٹ منظمین زبان | وڈے شہراں وچ بولنے والےآں دی اندازہً تعداد |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ویلش زبان | Cymraeg | بریطانی | 562,000 (19.0% ویلز دی آبادی کا) دعوی کردے نيں کہ اوہ "ویلش بول سکدے نيں" (2011)[۹][۱۰] | تقریباً 947,700 (2011) کل متکلمین — ویلز: 788,000 متکلمین، 26.7% ویلز دی آبادی کا،[۹][۱۰] — انگلستان: 150,000[۱۱] — صوبہ چوبوت، ارجنٹائن: 5,000[۱۲] — ریاستہائے متحدہ امریکا: 2,500[۱۳] — کینیڈا: 2,200[۱۴] |
ویلز; Y Wladfa، صوبہ چوبوت |
— Welsh Language Commissioner (Meri Huws) — The Welsh Government (previously the Welsh Language Board، Bwrdd yr Iaith Gymraeg) |
کارڈف: 54,504 سوانزی: 45,085 نیوپورٹ، ویلز: 18,490[۱۵] بینگور، گوینڈ: 7,190 |
| آئرش زبان | Gaeilge/ Gaedhilge | گویڈیلک | 40,000–80,000[۱۶][۱۷][۱۸][۱۹] جمہوریہ آئرلینڈ وچ ، 94,000 لوک آئرش روزانہ تعلیم دے نظام توں علاوہ استعمال کردے نيں۔[۲۰] |
1,887,437 جمہوریہ آئرلینڈ: 1,774,437[۲۰] مملکت متحدہ: 95,000 ریاستہائے متحدہ امریکا: 18,000 |
جمہوریہ آئرلینڈ | Foras na Gaeilge | ڈبلن: 184,140 گالوے: 37,614 کورک (شہر): 57,318[۲۱] بیلفاسٹ: 30,360[۲۲] |
| بریٹن زبان | brezhoneg | بریطانی | 206,000 | 356,000[۲۳] | بریتانیہ | Ofis Publik ar Brezhoneg | رین: 7,000 بریسٹ، فرانس: 40,000 نانت: 4,000[۲۴] |
| اسکاٹش گیلک | Gàidhlig | گویڈیلک | 57,375 (2011)[۲۵] اسکاٹ لینڈ وچ تے 1,275 (2011) نووا سکوشیا وچ [۲۶] | 87,056 (2011)[۲۵] اسکاٹ لینڈ وچ | اسکاٹ لینڈ | Bòrd na Gàidhlig | گلاسگو: 5,726 ایڈنبرگ: 3,220[۲۷] ابرڈین: 1,397[۲۸] |
| کورنش زبان | Kernowek | بریطانی | نامعلوم[۲۹] | 3,000[۳۰] | کورنوال | Cornish Language Partnership (Keskowethyans an Taves Kernewek) | ٹرورو: 118[۳۱] |
| مینکس زبان | Gaelg/ Gailck | گویڈیلک | 100+،[۳۲][۳۳] بشمول اک قلیل تعداد وچ بچے جو نويں مقامی بولنے والے نيں[۳۴] | 1,823[۳۵] | آئل آف مین | Coonceil ny Gaelgey | ڈگلس: 507[۳۶] |
جدول موازنہ
[سودھو]| ویلش | کورنش | بریٹن | آئرش | سکاٹش گیلک | مینکس | انگریزی |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gwenynen | gwenenen | gwenanenn | beach | seillean, beach | shellan | bee |
| cadair | kador | kador | cathaoir | cathair, seidhir | caair | chair |
| caws | keus | keuz | cáis | càis(e) | caashey | cheese |
| aber | aber | aber | inbhear | inbhir | inver | estuary, mouth of a river |
| llawn | leun | leun | lán | làn | lane | full |
| gafr | gaver | gavr | gabhar | gobhar | goayr | goat |
| tŷ | chi | ti | teach, tigh | taigh | thie | house |
| gwefus | gweus | gweuz | liopa, beol | bile, lip | meill | lip (anatomical) |
| arian, prês | mona, arhans | moneiz, arcʼhant | airgead | airgead | argid | silver, money |
| nos | nos | noz | oíche | oidhche | oie | night |
| rhif, nifer | niver | niver | uimhir | àireamh | earroo | number |
| tu mas, tu allan | yn-mes | er-maez | amuigh | a-muigh | mooie | outside |
| gellygen, peren | peren | perenn | piorra | peur/piar | peear | pear |
| chwarel, mwynglawdd | mengleudh | mengleuz | cairéal | coireall, cuaraidh | quarral | quarry, mine |
| ysgol | skol | skol | scoil | sgoil | scoill | school |
| seren | steren | steredenn | réalta | reul, rionnag | rollage | star |
| heddiw | hedhyw | hiziv | inniu | an-diugh | jiu | today |
| cwympo | kodha | kouezhañ | tit(im) | tuit(eam) | tuitt(ym) | (to) fall |
| ysmygu | megi | mogediñ, butuniñ | caith(eamh) tobac | smocadh | toghtaney, smookal | (to) smoke |
| chwibanu | hwibana | c'hwibanat | feadáil | fead | fed | (to) whistle |
حوالے
[سودھو]- ↑ (2013) "Celtic", Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- ↑ "American Heritage Dictionary. Celtic: kel-tik, sel"۔ Dictionary.reference.com۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 19 اگست 2011
- ↑ The Celtic languages:an overview، Donald MacAulay, The Celtic Languages، ed. Donald MacAulay, (Cambridge University Press, 1992)، 3.
- ↑ "Language by State – Scottish Gaelic" Archived 11 January 2012 at the وے بیک مشین on Modern Language Association website. Retrieved 27 December 2007
- ↑ "Languages Spoken At Home" Archived 25 March 2009 at the وے بیک مشین from Australian Government Office of Multicultural Interests website. Retrieved 27 December 2007; G. Leitner, Australia's Many Voices: Australian English--The National Language, 2004, pg. 74
- ↑ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO, 34, 365–366, 529, 973, 1053. Retrieved on 15 June 2010.
- ↑ "A brief history of the Cornish language"۔ Maga Kernow۔ ۲۵ دسمبر ۲۰۰۸ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ
- ↑ Beresford Ellis, Peter (1990, 1998, 2005). The Story of the Cornish Language. Tor Mark Press, 20–22. ISBN 0-85025-371-3.
- ↑ ۹.۰ ۹.۱ "Welsh language skills by local authority, gender and detailed age groups, 2011 Census"۔ StatsWales website۔ Welsh Government۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 13 نومبر 2015
- ↑ ۱۰.۰ ۱۰.۱ Office for National Statistics 2011 http://ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/census/2011-census/key-statistics-for-unitary-authorities-in-wales/stb-2011-census-key-statistics-for-wales.html#tab---Proficiency-in-Welsh
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees۔ "World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples – UK: Welsh"۔ UNHCR۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 23 مئی 2010
- ↑ "Wales and Argentina"۔ Wales.com website۔ Welsh Assembly Government۔ 2008۔ 16 اکتوبر 2012 وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 23 جنوری 2012
- ↑ "Table 1. Detailed Languages Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and Over for the United States: 2006–2008 Release Date: اپریل 2010" (xls)۔ ریاستہائے متحدہ مردم شماری بیورو۔ 27 اپریل 2010۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 2 جنوری 2011
- ↑ "2006 Census of Canada: Topic based tabulations: Various Languages Spoken (147)، Age Groups (17A) and Sex (3) for the Population of Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2006 Census – 20% Sample Data"۔ Statistics Canada۔ 7 دسمبر 2010۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 3 جنوری 2011
- ↑ StatsWales۔ "Welsh language skills by local authority, gender and detailed age groups, 2011 Census"۔ Welsh Government۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ "Irish Examiner"۔ Archives.tcm.ie۔ 24 نومبر 2004۔ 19 جنوری 2005 وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 19 اگست 2011
- ↑ Christina Bratt Paulston. Linguistic Minorities in Multilingual Settings: Implications for Language Policies. J. Benjamins Pub. Co, 81. ISBN 1-55619-347-5.
- ↑ Pierce, David (2000). Irish Writing in the Twentieth Century. Cork University Press, 1140. ISBN 1-85918-208-9.
- ↑ Ó hÉallaithe, Donncha (1999). . Cuisle.
- ↑ ۲۰.۰ ۲۰.۱ www.cso.ie Central Statistics Office, Census 2011 – This is Ireland – see table 33a
- ↑ Central Statistics Office۔ "Population Aged 3 Years and Over by Province County or City, Sex, Ability to Speak Irish and Census Year"۔ Government of Ireland۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ Department of Finance and Personnel۔ "Census 2011 Key Statistics for Northern Ireland" (PDF)۔ The Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل (PDF) توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ سانچہ:Fr icon Données clés sur breton, Ofis ar Brezhoneg
- ↑ Pole Études et Développement Observatoire des Pratiques Linguistiques۔ "Situation de la Langue"۔ Office Public de la Langue Bretonne۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ ۲۵.۰ ۲۵.۱ 2011 Scotland Census، Table QS211SC.
- ↑ "National Household Survey Profile, Nova Scotia, 2011"۔ Statistics Canada۔ 11 ستمبر 2013۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 7 جون 2014
- ↑ Scotland's Census۔ "Standard Outputs"۔ National Records of Scotland۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ Alison Campsie۔ "New bid to get us speaking in Gaelic"۔ The Press and Journal۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ See کورنش زبان
- ↑ Around 2,000 fluent speakers. "'South West:TeachingEnglish:British Council:BBC". BBC/British Council website (BBC). 2010. https://web.archive.org/web/20100108190250/http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/uk-languages/south-west. Retrieved on 9 فروری 2010.
- ↑ Equalities and Wellbeing Division۔ "Language in England and Wales: 2011"۔ Office for National Statistics۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- ↑ سائیٹ غلطی: نا منیا جان والا
<ref>ٹیگ کوئی لکھت نئیں دتی گئی اتے پتےiomtoday.co.imلئی۔ - ↑ Lua error in ماڈیول:Citation/CS1/Date_validation/ar at line 45: attempt to compare number with nil.
- ↑ "Documentation for ISO 639 identifier: glv"۔ Sil.org۔ 14 جنوری 2008۔ 28 جولائی 2011 وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 19 اگست 2011
- ↑ "Isle of Man Census Report 2011" (PDF)۔ Economic Affairs Division, Isle of Man Government Treasury۔ اپریل 2012۔ صفحہ: 27۔ 5 نومبر 2013 وچ اصل (PDF) توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 9 جون 2014
- ↑ Sarah Whitehead۔ "How the Manx language came back from the dead"۔ دی گارڈین۔ ۰۷ جنوری ۲۰۱۹ وچ اصل توں آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتریخ 6 مارچ 2016
- Ball, Martin J. & James Fife (ed.) (1993)۔ The Celtic Languages۔ London: Routledge. سانچہ:آئی ایس بی این۔
- Borsley, Robert D. & Ian Roberts (ed.) (1996)۔ The Syntax of the Celtic Languages: A Comparative Perspective۔ Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. سانچہ:آئی ایس بی این۔
- Cowgill, Warren (1975). "The origins of the Insular Celtic conjunct and absolute verbal endings", in H. Rix: Flexion und Wortbildung: Akten der V. Fachtagung der Indogermanischen Gesellschaft, Regensburg, 9.–14. ستمبر 1973. Wiesbaden: Reichert, 40–70. ISBN 3-920153-40-5.
- Celtic Linguistics, 1700–1850 (2000)۔ London; New York: Routledge. 8 vols comprising 15 texts originally published between 1706 and 1844.
- Forster, Peter; Toth, Alfred (جولائی 2003). "Toward a phylogenetic chronology of ancient Gaulish, Celtic, and Indo-European". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 (15): 9079–84. doi:. PMID 12837934. PMC: 166441. Bibcode: 2003PNAS.۔100.9079F. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12837934.
- Gray, Russell D.; Atkinson, Quintin D. (نومبر 2003). "Language-tree divergence times support the Anatolian theory of Indo-European origin". Nature 426 (6965): 435–39. doi:. PMID 14647380. Bibcode: 2003Natur.426.۔435G.
- Hindley, Reg (1990). The Death of the Irish Language: A Qualified Obituary. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-04339-5.
- Lewis, Henry & Holger Pedersen (1989)۔ A Concise Comparative Celtic Grammar۔ Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. سانچہ:آئی ایس بی این۔
- McCone, Kim (1991). "The PIE stops and syllabic nasals in Celtic". Studia Celtica Japonica 4: 37–69.
- McCone, Kim (1992). "Relative Chronologie: Keltisch", in R. Beekes: Rekonstruktion und relative Chronologie: Akten Der VIII. Fachtagung Der Indogermanischen Gesellschaft, Leiden, 31 اگست – 4 ستمبر 1987. Institut für Sprachwissenschaft der Universität Innsbruck, 12–39. ISBN 3-85124-613-6.
- McCone, K. (1996). Towards a Relative Chronology of Ancient and Medieval Celtic Sound Change. Maynooth: Department of Old and Middle Irish, St. Patrick's College. ISBN 0-901519-40-5.
- Russell, Paul (1995). An Introduction to the Celtic Languages. Longman. ISBN 0-582-10082-8.
- Schmidt, K.H. (1988). "On the reconstruction of Proto-Celtic", in G. W. MacLennan: Proceedings of the First North American Congress of Celtic Studies, Ottawa 1986. Ottawa: Chair of Celtic Studies, 231–48. ISBN 0-09-693260-0.
- Schrijver, Peter (1995). Studies in British Celtic historical phonology. Amsterdam: Rodopi. ISBN 90-5183-820-4.
- (2004) Die keltischen Primärverben. Ein vergleichendes, etymologisches und morphologisches Lexikon (in German). Innsbruck: Institut für Sprachen und Kulturen der Universität Innsbruck. ISBN 3-85124-692-6.
باہرلے جوڑ
[سودھو]| کیلٹی بولیاں دے بارے چ ہور جانن لئی وکیپیڈیاساتھی منصوبے: | |
| ڈکشنری وکشنری توں | |
| مشترکہ زریعے کومنز توں | |
| آزاد تعلیمی موادتے مصروفیات ویکیورسٹی توں | |
| آزاد کتاب گھر ویکی منبع توں | |
| آزاد نصابی تے دستی کتاباں ویکی کتاباں توں | |
- سانچہ:Dmoz
- Aberdeen University Celtic Department
- "Labara: An Introduction to the Celtic Languages"، by Meredith Richard
- Celts and Celtic Languages
- What is necessary to decide if Lusitanian is a Celtic language?
|
- مضامین جنہاں وچ اردو بولی دا متن شامل اے
- Language articles with unsupported infobox fields
- مضامین جنہاں وچ ویلش بولی دا متن شامل اے
- مضامین جنہاں وچ آئرستانی بولی دا متن شامل اے
- مضامین جنہاں وچ بریٹن بولی دا متن شامل اے
- مضامین جنہاں وچ غیلیہ اسكتلندیہ بولی دا متن شامل اے
- مضامین جنہاں وچ كورنیہ بولی دا متن شامل اے
- مضامین جنہاں وچ مینکس بولی دا متن شامل اے
- ویکیپیڈیا مضامین مع LCCN شناخت کنندگان
- ویکیپیڈیا مضامین مع GND شناخت کنندگان
- ویکیپیڈیا مضامین مع BNF شناخت کنندگان
- کیلٹک زباناں
- ہند یورپی زباناں
- سیلٹی بولیاں
- ہند یورپی بولیاں
- Pages using PMID magic links
